News — Graphene
Graphene based batteries are lighter, more durable with higher capacity of energy storage.
Posted by MSE Supplies on
The potential of graphene for batteries becomes more and more obvious. Recently, Saint Jean Carbon announced that it has started the design and build of graphene based lithium-ion batteries. SJC Stated that a single layer of g...
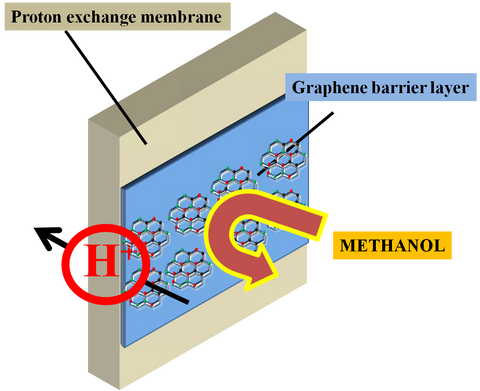
CVD Single Layer Graphene Significantly Enhances Fuel Cell Efficiency
Posted by MSE Supplies on
Graphene is increasingly studied as a promising platform for developing novel separation technologies in applications such as fuel cells. This interest has arisen because graphene is a maximally thin membrane that, once perfor...
Ultralight mechanical watch enabled by graphene
Posted by MSE Supplies on
An ultralight high-performance mechanical watch made with graphene is unveiled today in Geneva at the Salon International De La Haute Horlogerie thanks to a unique collaboration. The University of Manchester has collaborated wi...
Functional OLED electrodes are produced from graphene for the first time
Posted by MSE Supplies on
For the first time, it has been possible to produce functional OLED electrodes from graphene. The process was developed by Fraunhofer researchers together with partners from industry and research. The OLEDs can, for example, ...
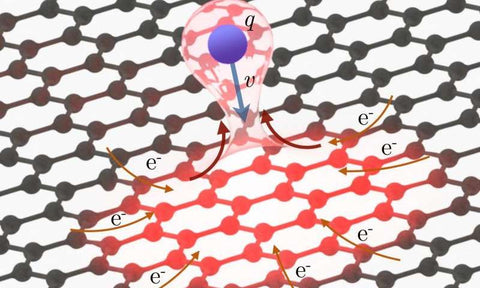
Graphene is Proven to be an Enabler of Ultra-fast Electronics
Posted by MSE Supplies on
The strong electric field of the highly charged ions is able to tear dozens of electrons away from the graphene within a matter of femtoseconds. However, because graphene is able to transport high electric currents, the positiv...